There are a lot of different stuff in African cultures, and
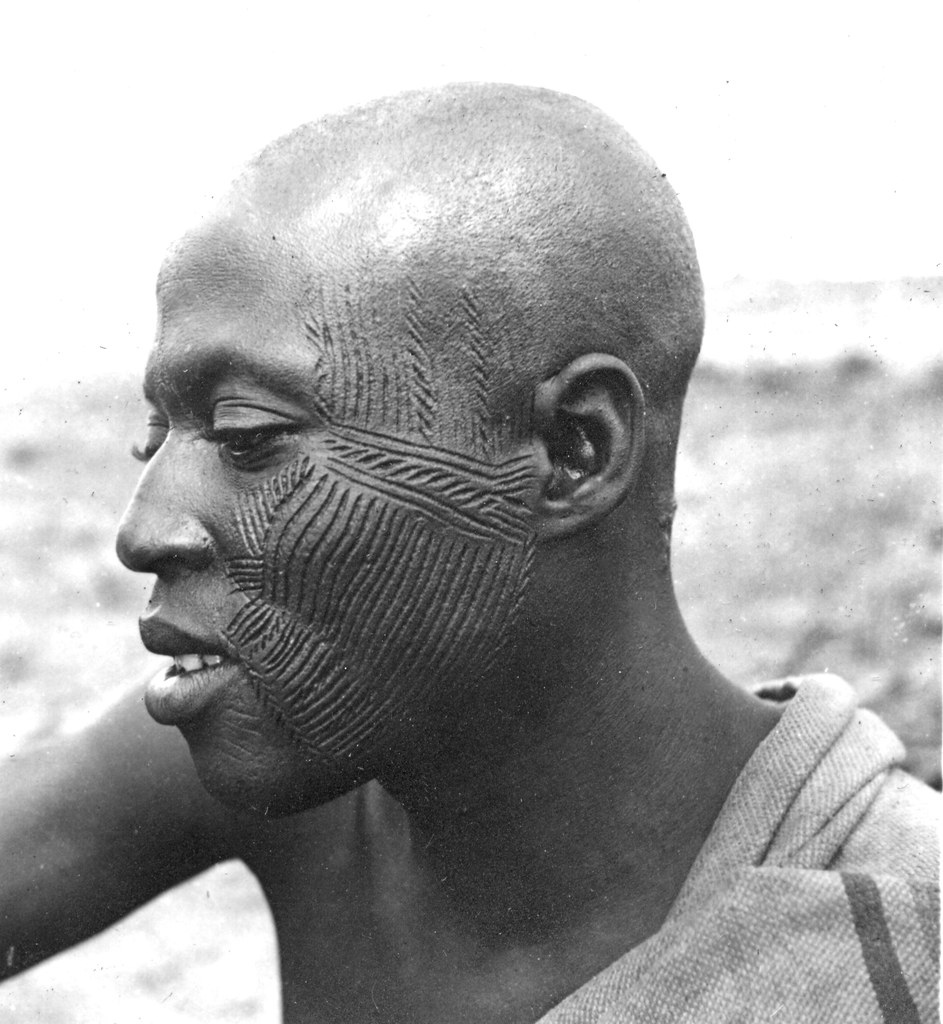
one of the main things is SCARIFICATION, along with their hairstyles and so on.
Scarification is done on the human body, not on other
objects like their art in pottery, but as one can notice the patters and
shapes/forms are related to each other. This is a cultural activity which a lot
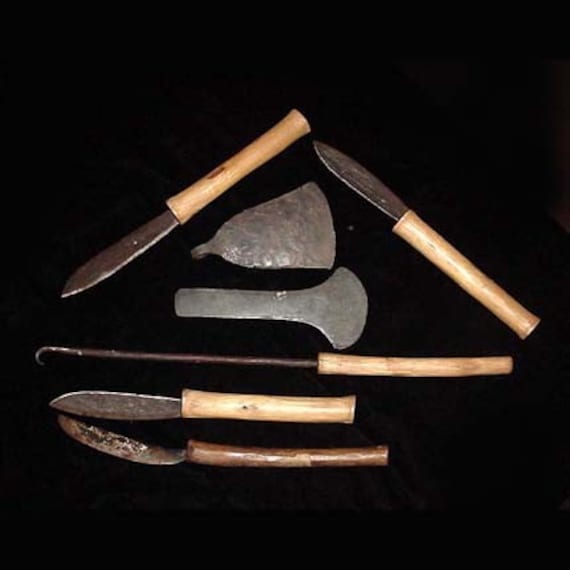
of tribes perform this act in Africa, this is done when the artist does cuts on
the body with a sharp tool, where as a tool one uses a knife, stone, coconut
shell or a stone where this tool is generally used to control the shapes of the
scars as they are sometimes different in every body part.
Scarification tools
Cicatrisation is a different type of scarification, it is
done where a wound is made through the skin with a sharp object and then they’ll
apply certain juices from an caustic pland and permanent blisters will form,
yet they’ll even perform some kind of tattooing where some of them will rub the
wound with gunpowder or charcoal found from the ground and when they’ll heal
they’ll be marked forever. The cut marks, will be called KELOIDS once they’’ be
healed.
Performing Cicatrisation
This is a painful and a long process, where it’s a permanent
mark that’s why its called a modification, yet they’ll still do it as it sends
messages or gives identity of the tribe where their meanings are generally
about politics, religious or social things. Just like in West Africa, they’ll
do them for identity of the groups or family or even individuality yet if not
about the ones I mentioned, they’ll do them for expressing beauty. They even
perform body scarification on women, where they represent stages of one’s life
just like puberty and marriage.
Stages of life scarification
On men, when they make facial scarification, they’ll do them
so one will be attractive as one can touch and to look at and women sometime
will do them aswell to show their strong resistance to childbirth.
In other countries like Nigeria, woman with scared faces
will show their demand to sex, where woman will show that they are willing for a
lot of children, this is because they’ll say that one will have more erotic sensations
when they’re touched by men as scars will stay sensitive for many years till
they’ll heal completely
Yet, one should know that multiple scarifications are for
decorations in different social parts. As today this is changing in Africa as a
lot of tribes are NOT using scars patterns anymore and can only be seen on the
elderly.